Molecular Orbital For C2. Calculate the bond order for your molecule. What is the molecular orbital of c2?
On the basis of molecular orbital theory (mot), it has electronic configuration = sigma 1s2 ( bonding orbitals) ,sigma*1s2 (antibonding orbitals), sigma 2s2 (b. From the molecular orbital electronic configuration, number of electrons present in pi orbitals present is equal to 2. This gives a bond order of 2, which means that there should exist a double bond between the two carbons in a ${c_2}$.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Carbon Dimer C2Fill From The Bottom Up With 8 Electrons Totalbonding Order Is 2 And It Is Diamagneticsigma2S2Sigma2S.
1.) o*2p 2.) pie *2p Is c2 paramagnetic according to. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as co.
Of All The Possible Molecular Orbitals In A Structure, Two.
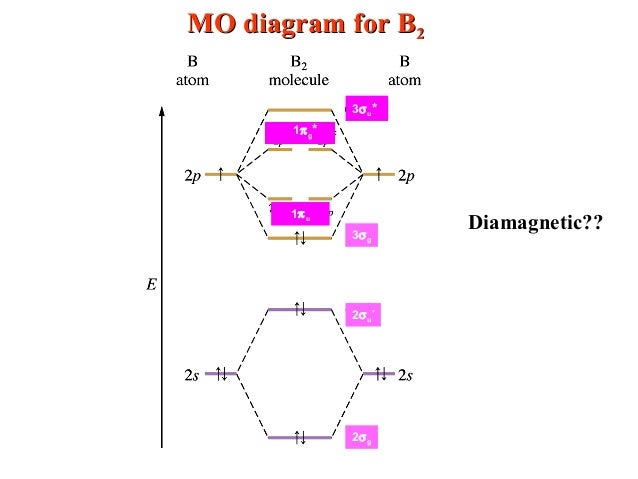
Write the molecular orbital configuration for your molecule. The c 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding.
From The Molecular Orbital Electronic Configuration, Number Of Electrons Present In Pi Orbitals Present Is Equal To 2.
On the basis of molecular orbital theory (mot), it has electronic configuration = sigma 1s2 (bonding orbitals) ,sigma*1s2 (antibonding orbitals), sigma 2s2 (b.orbitals),sigma *2s2 (anti bonding orbitals), (pi bonding orbital )px2= (pi bonding orbital )py2. Molecular orbitals of the second energy level. Place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of b2, c2, and n2.
Energy Molecular Orbital (Σ*) Will Be Empty (Recall The Aufbau Principle).
When molecular orbitals form, two valence electrons are required to be situated in between two atoms for a molecular orbital, forming a chemical bond. Molecular orbital theory shows that it has two sets of paired electrons in a degenerate bonding set of orbitals. O2 and f2 is an.
If We Arbitrarily Define The Z Axis Of The Coordinate System For The O 2 Molecule As The Axis Along Which The Bond Forms, The 2P Z.
An electron in atomic orbital is under the influence of only one positive nucleus of. This diagram should be to scale. Σ z y x σ* x y z construct the molecular orbital diagram for.
Related Posts
- Difference Between Ionic Compound And Molecular CompoundDifference Between Ionic Compound And Molecular Compound. The main difference between both compounds is that ionic compounds are formed by the transf ...
- Magnesium Nitrite Trihydrate Molecular MassMagnesium Nitrite Trihydrate Molecular Mass. Mg(no2)2 is a white powder at room temperature. Molar mass of mg(no3)2 = 148.3148 g/mol.Lithium nitrate ...
- So42 Molecular GeometrySo42 Molecular Geometry. What type of bond is so42? Molecular geometry & polarity tutorial.Is SO42 Polar or Nonpolar? (sulfate ion) YouTube from ...
- Molecular Mass Of PbMolecular Mass Of Pb. Its atomic weight (average relative mass ) on the periodic table is 207.2. Convert grams pb (aso4)2 to moles or moles pb (aso4) ...
- Molecular Geometry Of Cocl2Molecular Geometry Of Cocl2. Pf3 has 26 valence electrons. 8 rows the chemical formula cocl2 represents cobalt (ii) chloride.Fosgene from www.lookfor ...
- Difference Between Molecular Compound And Ionic CompoundDifference Between Molecular Compound And Ionic Compound. Composition varies depending on the type of compound, but all ionic compounds must have a n ...
- Determine The Molecular Geometry Of Cbr4Determine The Molecular Geometry Of Cbr4. To carry out so, we an initial need to draw alewis framework for cbr4.because that this, we need to do the ...



